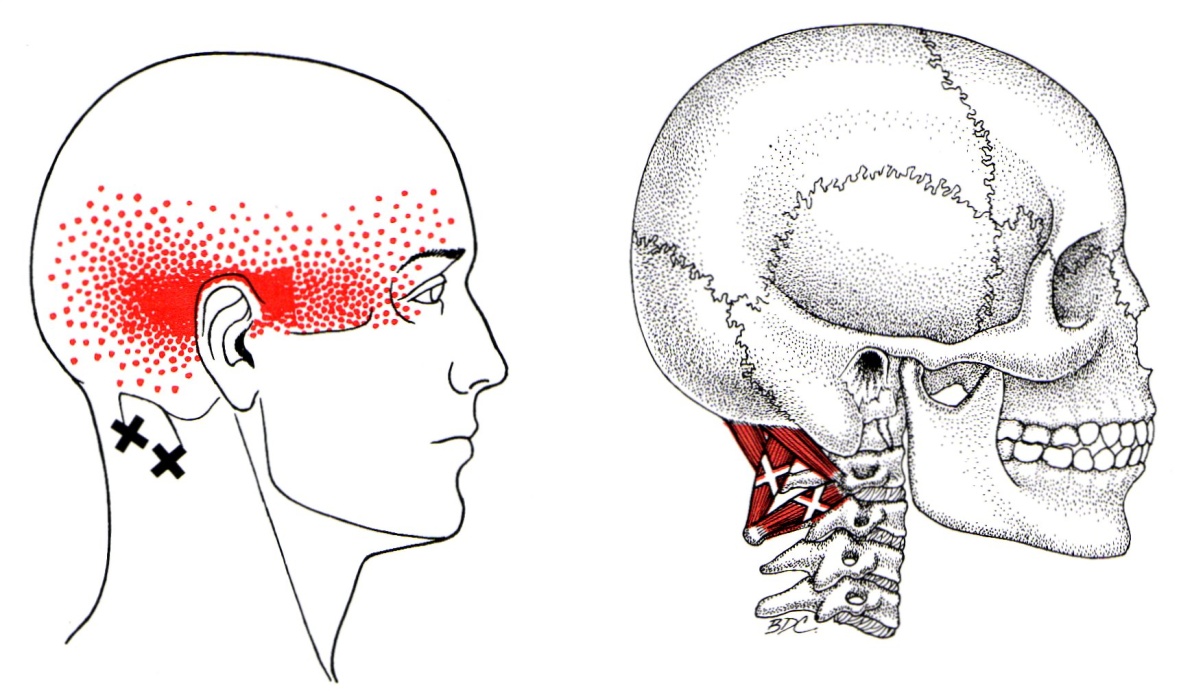
Suboccipital Referral Pattern
Suboccipital Referral Pattern - Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. If they are tense or carry active trigger points, they can trigger headaches and restrict the mobility of the neck. Web suboccipital muscles are responsible for head and neck movements and play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture. In particular, they initiate and control fine movements. Web the spot will normally be painful to compression and produce a stereotypical referral pattern to distant structures. Web along with lots of other neck muscles, the suboccipital group — usually just called “the suboccipitals” — work overtime to keep your head balanced on top of your spine. 32 myofascial trigger points of the scm have a similar referred pain pattern to that seen in cgh (posterior to frontal). You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Web a cervicogenic headache is thought to be referred pain arising from irritation caused by cervical structures innervated by spinal nerves c1, c2, and c3; 32 myofascial trigger points of the scm have a similar referred pain pattern to that seen in cgh (posterior to frontal). Web suboccipital muscles are responsible for head and neck movements and play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. Web the spot will normally be painful to compression and produce a stereotypical referral pattern to distant structures. Web along with lots of other neck muscles, the suboccipital group — usually just called “the suboccipitals” — work overtime to keep your head balanced on top of your spine. Web cervicogenic headache patients have a high probability of having myofascial trigger point pain, 54 particularly from overactivity of the scm, upper trapezius, and temporalis. Understanding suboccipital muscle trigger points. Proper diagnosis and treatment of suboccipital trigger points are essential for relieving pain and discomfort. Web a cervicogenic headache is thought to be referred pain arising from irritation caused by cervical structures innervated by spinal nerves c1, c2, and c3; Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and temporal bones. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. In particular, they initiate and control fine movements. Understanding suboccipital muscle trigger points. Web a cervicogenic headache is thought to be referred pain arising from irritation caused by cervical structures innervated by spinal nerves c1, c2, and c3; Referred pain patterns have been studied in healthy volunteers. Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and temporal bones. Web cervicogenic headache patients have a high probability of having myofascial trigger point pain, 54 particularly from overactivity of the scm, upper trapezius, and temporalis. Web the suboccipital muscles. Web cervicogenic headache patients have a high probability of having myofascial trigger point pain, 54 particularly from overactivity of the scm, upper trapezius, and temporalis. You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Web along with lots of other neck muscles, the suboccipital group — usually just called “the suboccipitals” — work overtime to keep your head balanced on top. Understanding suboccipital muscle trigger points. In particular, they initiate and control fine movements. Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. Referred pain patterns have been studied in healthy volunteers without neck pain as well as in those with proven cervical joint pain. If they are tense or carry active trigger points, they can trigger headaches and restrict the mobility of the neck. 32 myofascial trigger points of the scm have a similar referred pain pattern to that seen in cgh. Proper diagnosis and treatment of suboccipital trigger points are essential for relieving pain and discomfort. Understanding suboccipital muscle trigger points. In particular, they initiate and control fine movements. Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. Web suboccipital muscles are responsible for head and neck movements and play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture. Web along with lots of other neck muscles, the suboccipital group — usually just called “the suboccipitals” — work overtime to keep your head balanced on top of your spine. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. Web cervicogenic headache patients have a high probability of having myofascial trigger point pain, 54 particularly from. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Web cervicogenic headache patients have a high probability of having myofascial trigger point pain, 54 particularly from overactivity of the scm, upper trapezius, and temporalis. In particular, they initiate and control fine movements. Web activated trigger points on the. Web suboccipital muscles are responsible for head and neck movements and play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture. Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. Proper diagnosis and treatment of suboccipital trigger points are essential for relieving pain and discomfort. If they are tense or carry active trigger points, they can trigger headaches. Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. You can relieve these points and tensions yourself. Web suboccipital muscles are responsible for head and neck movements and play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture. Proper diagnosis and treatment of suboccipital trigger points are essential for relieving pain and discomfort. Web along with lots of. Travell and simons have divided tps into subtypes, including active, associated, attachment, central,. Web along with lots of other neck muscles, the suboccipital group — usually just called “the suboccipitals” — work overtime to keep your head balanced on top of your spine. Web the spot will normally be painful to compression and produce a stereotypical referral pattern to distant structures. Web the suboccipital muscles consist of four small muscles at your cervical spine. Web a cervicogenic headache is thought to be referred pain arising from irritation caused by cervical structures innervated by spinal nerves c1, c2, and c3; Understanding suboccipital muscle trigger points. Referred pain patterns have been studied in healthy volunteers without neck pain as well as in those with proven cervical joint pain. Proper diagnosis and treatment of suboccipital trigger points are essential for relieving pain and discomfort. Web suboccipital muscles are responsible for head and neck movements and play a crucial role in maintaining proper posture. In particular, they initiate and control fine movements. 32 myofascial trigger points of the scm have a similar referred pain pattern to that seen in cgh (posterior to frontal). Web activated trigger points on the suboccipital muscles can result in a referred pain pattern that spreads to one and/or both sides of the head above the occipital and temporal bones.Suboccipital Muscles Headaches, Migraines, Eye Pain The Wellness Digest
Suboccipital Trigger Point Release and Stretch Nourishing Massage
Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the
Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the
Alila Medical Media Trigger points and referred pain patterns for the
The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide 13
Suboccipital Group The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide
Suboccipital Group Trigger Points Learn Muscles
Suboccipital Muscles Trigger Points
The Trigger Point & Referred Pain Guide 13
If They Are Tense Or Carry Active Trigger Points, They Can Trigger Headaches And Restrict The Mobility Of The Neck.
You Can Relieve These Points And Tensions Yourself.
Web Cervicogenic Headache Patients Have A High Probability Of Having Myofascial Trigger Point Pain, 54 Particularly From Overactivity Of The Scm, Upper Trapezius, And Temporalis.
Related Post: